Setup Instance in Oracle Cloud
- Select the instance architecture
- Download Public and Private key
- Use image Amperage and oracle 9
- Copy public IP after the instance is created and running
Setup SSH access to the new instance created
Access from Windows using Putty
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/Tasks/accessinginstance.htm
- convert .key file downloaded from OCI to .ppk key using PuTTYgen
- Use this ppk to connect as putty doesnt understand private key
Access from Visual Studio Code
- Install Remote extension for SSH in VSCode
- Open the SSH default SSH configuration file using Control + Shift + P
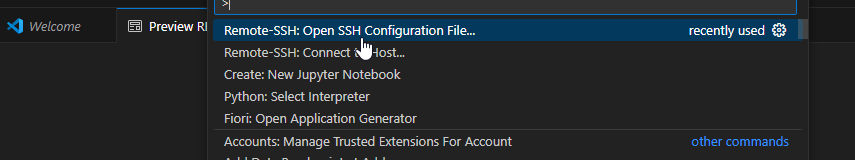
3. In VSCode private key can be directly used to connect. Maintain the location of private key in the SSH configuration file.
Host XXX.XXX.XX.XXX
User opc
HostName XXX.XXX.XX.XXX
IdentitiesOnly=yes
IdentityFile "C:\Users\xxxx\Downloads\ssh-key.key"4. Access root using command
$ sudo su - Create New User with root Access
sudo su - # Swich to root user
sudo adduser jo
sudo passwd jo
sudo usermod -aG wheel jo
Check if wheel is part of sudoers file if this the below entry is availalbe.
nano /etc/sudoers
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
Setup SSH access without password
sudo su - <User>
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 # Genearate SSH Keys and keys are saved in /home/<user>/.ssh folderEnsure .ssh folder has access 700
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
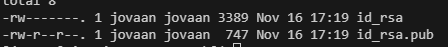
Copy generated public key to authorized key folder
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Ensure access for authorized key folder : Should be 600
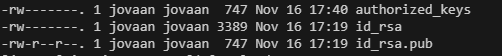
Note : SSH folder authorization is critical for proper authentication. .SSH folder should be set at 700 and autorized_key , id_rsa at 600
Activate Public key authorization in /etc/ssh/sshd_config .
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
PubkeyAuthentication yes
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys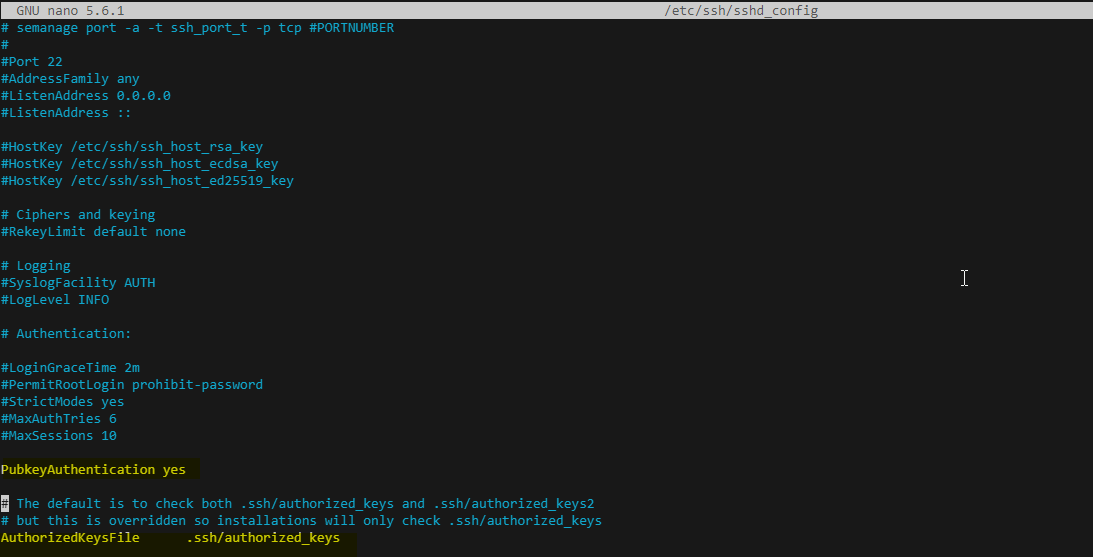
sudo systemctl restart sshd
ssh jovaan@<hostname>
connect using Visual Studio Code
down the id_rsa file from ~/.ssh and add to SSH configuration file.
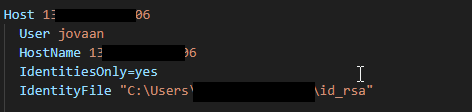
For using putty upload id_rsa key and generate .ppk key .
How to modify Sever Host Name
To change the hostname on Oracle Cloud Linux, follow these steps. These steps work on Oracle Linux as well as most RHEL-based distributions.
1. Temporarily Change the Hostname
To change the hostname for the current session (this will reset after a reboot):
bashCopy codesudo hostnamectl set-hostname new-hostname
Replace new-hostname with your desired hostname.
2. Permanently Change the Hostname
To make the hostname change persist after a reboot, follow these steps:
Update the Hostname using hostnamectl
- Use
hostnamectlto set the new hostname:bashCopy codesudo hostnamectl set-hostname new-hostname - Verify the change:bashCopy code
hostnamectl
Update the /etc/hosts File
- Open
/etc/hostsin a text editor:bashCopy codesudo nano /etc/hosts - Find the line with the old hostname, and replace it with the new hostname. The line should look similar to this:plaintextCopy code
127.0.0.1 localhost new-hostname - Save and close the file.
Reboot (Optional)
To ensure all services recognize the new hostname, reboot the server:
sudo reboot
After the reboot, the hostname should be updated across all sessions and services. You can verify it with:
hostname
hostnamectl
Note:
If you are using cloud-init (common in cloud environments), you may need to update cloud-init configuration files to prevent it from overwriting your changes on boot.
Change Hostname in Oracle Cloud
1. In the file /etc/oci-hostname.conf change the value of PRESERVE_HOSTINFO to 2.
/etc/oci-hostname.conf
PRESERVE_HOSTINFO=2
This change will be persistent across reboots.
2.Edit /etc/sysconfig/network
change the parameter value for “hostname”
# cat /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=<new_hostname> ← — — — — change here
3.Update the /etc/hostname file with the below command.
hostnamectl set-hostname <new_hostname>
Pyspark in Venv
- Create new virutal env
- python3 -m venv <env>
- Activate Virtual env
- source dev/env/bin/activate
- pip install pyspark
- Check pyspark version
- python -c “import pyspark; print(pyspark.version)”
- type pyspark to start pyspark in python
- if successful the following screen should dispaly
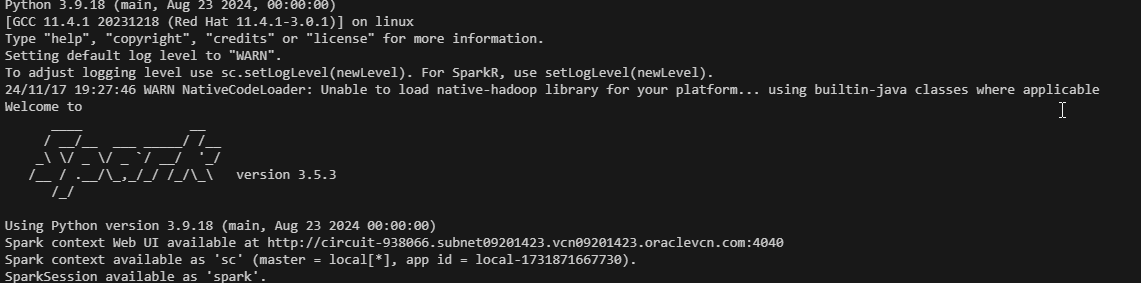
## Sample spark code
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("MyApp") \
.getOrCreate()
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
("sue", 32),
("li", 3),
("bob", 75),
("heo", 13),
],
["first_name", "age"],
)
df.show()
Error Management : Pyspark
pyspark.errors.exceptions.base.PySparkRuntimeError: [JAVA_GATEWAY_EXITED] Java gateway process exited before sending its port number.
Reason : Java not installed or Java_Home not set
- $ which java
- this will give you the latest java installed
- if java is not installed
- sudo dnf install java-11-openjdk -y
- after installation check java path : java -version
- $which java
- this will display the path of java files
- $ readlink -f $(which java)
- Will display the exact java path user eg : /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-11.0.25.0.9-2.0.1.el9.aarch64/bin/java
- Setting up JAVA_HOME
- $ nano ~/.bashrc
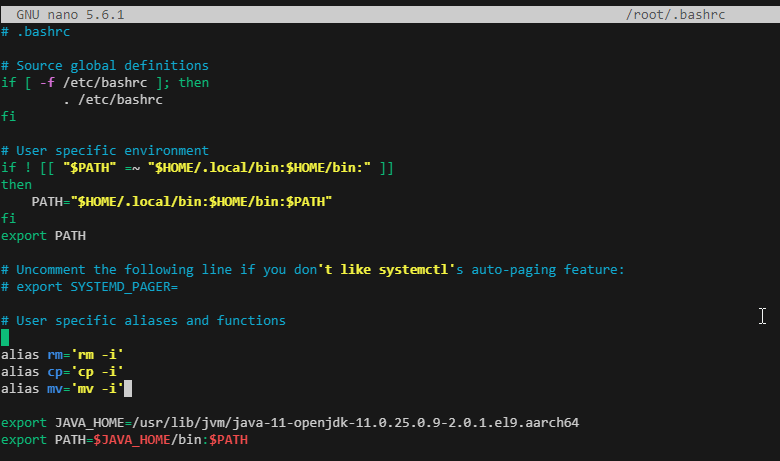
$ source ~/.bashrc ## Activate without restarting
$ which java ## This shoud show java path mentioned in the environment variable.
Install Django
pip install django
python -m django –version ## Check version after installation
How to setup visual studio code debugger for django
https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/tutorial-django
Activate Apache Server for Oracle Linux 9
- 1. sudo systemctl start httpd
- 2. sudo systemctl enable httpd
- sudo systemctl status httpd
- Port 80 Firewall
- sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service=http
- sudo firewall-cmd –reload
- Port 443 Firewall
- sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service=https
- sudo firewall-cmd –reload
- sudo systemctl restart httpd
- After starting Apache, test it by navigating to your server’s IP address or domain in a web browser. You should see the Apache default welcome page if it’s working correctly.
- Note
- if /var/www/html/index.html is not available then Apache standard page is loaded
- if maintained index.html is loaded
- Adjust SELinux Settings
- sestatus
- if status is enforcing then not enforce only for testing purposes.
- sudo setenforce 0
Other Related Commands
- sudo systemctl stop httpd
- sudo systemctl disable httpd
- sudo apachectl configtest
- sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log
- curl localhost can be used t check if the page is displayed properly
Locations of Apache files
- sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf ## Main config file
- DocumentRoot “/var/www/html”
Error Messages
AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server’s fully qualified domain name,
- sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- ServerName myserver.example.com ## Maintain server name in the file
- systemctl restart httpd
Encrpt for https access using lets encrpt
- sudo yum install epel-release
- sudo yum update
- sudo yum install snapd
- If snapd install failed follow the below
- nano /etc/yum.repos.d/oracle-epel-ol9.repo
- change : “enabled=0” to “1”
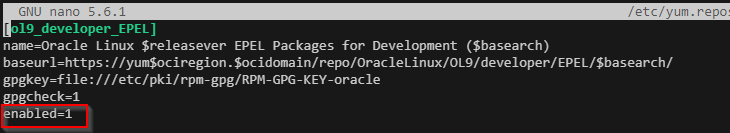
- yum remove certbot* -y
- dnf install oracle-epel-release-el9 -y
- dnf install snapd -y
- systemctl enable snapd
- systemctl start snapd
- snap install core; sudo snap refresh core
- sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap
- snap install –classic certbot
- ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
- certbot –apache
- certbot renew –dry-run
- echo -e “\n12 34 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew” >> /etc/crontab
https://forum.snapcraft.io/t/no-match-for-argument-snapd/35575
Apache Gunicorn Setup for webserver
- Navigate to virtual env and install gunicorn :
- pip install gunicorn
- Login in as root and install apache addon
- sudo su –
- sudo dnf install httpd -y # Use apt for Ubuntu or Debian
- sudo systemctl start httpd
- sudo systemctl enable httpd
- Check if the following apache modules are installed
- ls /etc/httpd/modules | grep -E ‘proxy|headers|rewrite’
- mod_headers.so
- mod_proxy_ajp.so
- mod_proxy_balancer.so
- mod_proxy_connect.so
- mod_proxy_express.so
- mod_proxy_fcgi.so
- mod_proxy_fdpass.so
- mod_proxy_ftp.so
- mod_proxy_hcheck.so
- mod_proxy_http2.so
- mod_proxy_http.so
- mod_proxy_scgi.so
- mod_proxy.so
- mod_proxy_uwsgi.so
- mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
- mod_rewrite.so
- if the modules are not found then
- sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- Uncomment the following lines
- LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
- LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
- LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.so
- LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
- ls /etc/httpd/modules | grep -E ‘proxy|headers|rewrite’
- Navigate to Django Project directory and run the following command
- gunicorn –workers 3 –bind 0.0.0.0:8000 myproject.wsgi:application
- Create new gunicorn service for managing from systemctl
- sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gunicorn.service
[Unit]
Description=gunicorn daemon for Django project
After=network.target
[Service]
User=your_user
Group=your_user
WorkingDirectory=/path/to/your/project
ExecStart=/path/to/your/venv/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/run/gunicorn.sock myproject.wsgi:application
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Start and enable Gunicorn service
- sudo systemctl start gunicorn
- sudo systemctl enable gunicorn
- if gunicron file is changed use the following commands to restart
- sudo systemctl restart gunicorn
- systemctl daemon-reload
Setting up Apache server with Gunicorn reverse proxy
- sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/myproject.conf
Installing Hadoop
sudo yum update
Install oracle : open jdk
Create new user for Hadoop
- sudo adduser hdoop
- su – hdoop
- ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
- cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
- chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
- sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- PubkeyAuthentication yes
- AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
- sudo systemctl restart sshd
- ssh localhost
Download latest version of Hadoop
Login in as hadoop user and download package.
wget https://downloads.apache.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.4.1/hadoop-3.4.1.tar.gz
tar xzf hadoop-3.4.1.tar.gz
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/install-hadoop-ubuntu
Error Msg
Not able to find command : JPS
$ sudo yum install ant
: org.apache.hadoop.security.AccessControlException: Permission denied: user=XXXX, access=WRITE, inode="/":hadoop:supergroup:drwxr-xr-x
How to setup hadoop super user
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.jo.groups</name>
<value>*</value> <!-- Allow jo to proxy any group -->
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.jo.hosts</name>
<value>*</value> <!-- Allow jo to proxy from any host -->
</property>
Can’t Delete HDFS Directory Via Web Interface Because I’m Dr. Who
In case anyone is still looking at this, you can set your user by setting the property in the core-site.xml as such
<configuration>
...
<property>
<name>hadoop.http.staticuser.user</name>
<value>youruserhere</value>
</property>
...
</configuration>
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47310619/cant-delete-hdfs-directory-via-web-interface-because-im-dr-whoFrequently used Hadoop commands
https://docs.cloudera.com/cdsw/1.10.5/cdsw-on-hdp/topics/cdsw-create-hdfs-user-directories.html
- hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/admin
- hdfs dfs -ls /path/to/directory
- hdfs dfs -mkdir /path/to/new_directory
- hdfs dfs -rm -r /path/to/directory_or_file
- hdfs dfs -put /local/path/file.txt /hdfs/path/
- hdfs dfs -get /hdfs/path/file.txt /local/path/
- hdfs dfs -cat /path/to/file
- hdfs dfs -du -s -h /path/to/directory # Check Disk Usage
- hdfs dfs -mv /source/path/file.txt /destination/path/ # within HDFS
- hdfs dfs -mv /path/file1.txt /path/file2.txt # Rename File
- hdfs dfs -cp /source/path/file.txt /destination/path/
- hdfs dfs -chmod 755 /path/to/file_or_directory ## Change File Permission
- hdfs dfs -chown user:group /path/to/file_or_directory ## Change Ownership
- hdfs dfs -chgrp group /path/to/file_or_directory ## Change Group Ownership
- hdfs dfs -stat “%y” /path/to/file ## Fie or Directory status
- hdfs dfs -checksum /path/to/file
- hdfs dfs -count /path/to/directory # Count no of directory , file , bytes
- hdfs dfs -head /path/to/file ## First new line of file
- hdfs dfs -tail /path/to/file ## Last line
- hdfs dfsadmin -safemode get ## Safe Mode Status
- hdfs dfsadmin -safemode leave ## Leave safe mode
- hdfs dfsadmin -report ## HDFS Status
- hdfs dfs -ls /path/to/snapshot ## Snap Shot Status
0 Comments